SMT-QC
Prevent mounting defects;do not just solve them
Quality Control System
During the final product mounting process, product quality is based on a variety of complex factors: from the materials and components selected to the manufacturing equipment used and the setting conditions. Many companies conduct analysis after an implementation defect occurs to find the cause. However, it takes time to unravel these complex factors without back data. In the meantime, products at risk of defects continue to be sold, and the problems escalate. Therefore, instead of solving problems after they occur, evaluating each process and creating a system to prevent implementation defects is necessary.
Typical Problematic Scenarios
Mounting defects occur after mass production
After starting mass production and post-shipment, defects in reflow soldering become apparent. Due to negligent quality control, the cause of the defect remains unidentified, leading to an accumulation of defective products and complaints which results to a loss of profit and credibility.
Changes in mounting conditions during mass production
In order to correct mounting defects as soon as possible, a site with a defective product tries to change the temperature profile and solder amount as a symptomatic measure. However, these makeshift measures hardly bring any improvements, increasing the pressure.
Demanding quality assurance from suppliers
Unable to do anything on its own, the site submits a request for improvement to the relevant suppliers. However, since the cause of the problem is unclear, the responsibility for the problem is also ambiguous, leading to endless debates.
Ideal State
Preventive measures against reflow soldering defects prior to mass production
The site can preemptively mitigate the risk of reflow soldering defects by evaluating components, substrates, solder, and the conditions for solder printing, mounting, and reflow profiles during the development and prototyping phases before mass production. These measures prevent potential reflow soldering defect risks before manufacturing.
Monitoring quality variations during mass production
The quality of a material might change due to supplier variations, and often the purchaser is unaware of this. By conducting acceptance inspections, these shifts in quality can be detected early on, preventing potential reflow soldering defects.
Guaranteeing quality to customers
Provide quality assurance to customers based on objective back data gathered before and during mass production. Should reflow soldering defects arise, quick resolutions can be achieved by leveraging analytical results and providing feedback to the development and manufacturing sectors and suppliers.

The key is to prevent reflow soldering defects preemptively rather than address them after they have emerged.
Problem &
SolutionReflow soldering Related issues and Solutions
Issue with components and PCB
Openings, cracks, and head-in-pillow defects, which are common mounting defects at reflow soldering sites, are caused by changes in the coplanarity of component terminals and PCB warpage during heating. In order to prevent and improve these reflow soldering defects, it is necessary to understand the terminal coplanarity and PCB warpage at each temperature during reflow.
-
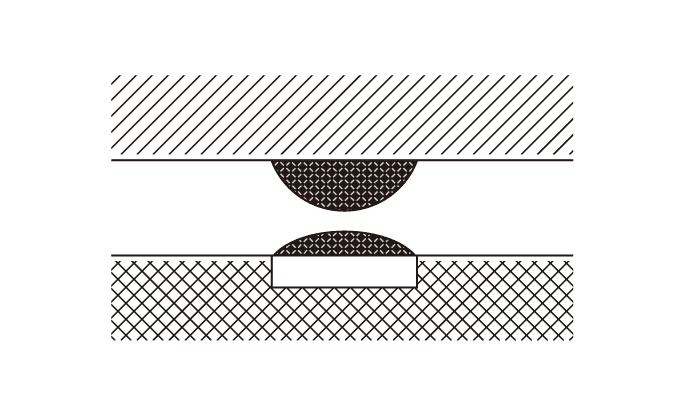 Open
OpenThese arise when the terminal and solder are not in contact at the point of solder solidification.
-
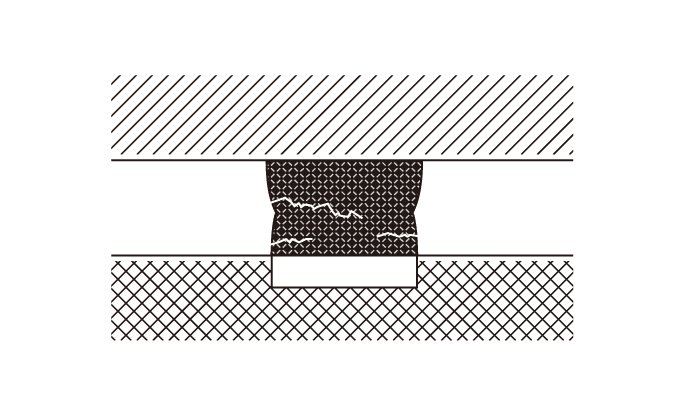 Cracks
CracksThese occur when the flatness and warpage increase after the solder solidification point and stress is applied.
-
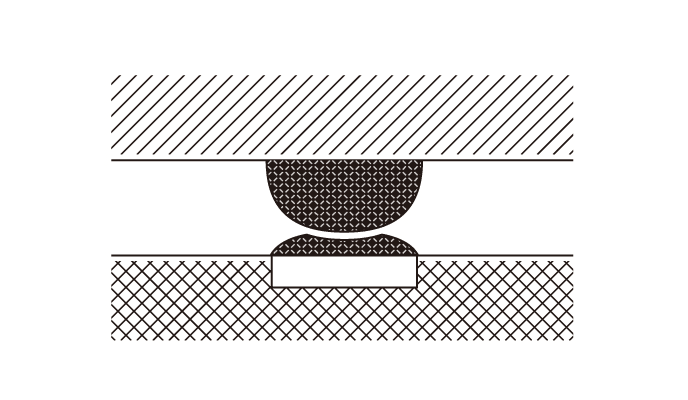 Head-in-pillow Soldering
Head-in-pillow SolderingThis is caused by solder oxidation as a result of high flatness and warpage before the solder solidification point.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
-
Measuring Component Coplanarity during Reflow
Heat causes changes in the terminal coplanarity of electronic components, including connectors and semiconductors. Therefore, it is necessary to select components based on the terminal coplanarity and warpage trends for each temperature in the in-house reflow profile to reduce the risk of defects.
-
Measuring PCB Warpage during Reflow
Like electronic components, boards also experience changes in warpage due to heat. The amount and tendency of warpage varies depending on the material, thickness, pattern bias, etc. Ideally, the amount of warpage should be reduced. However, if challenging to do so, strategies would need to align with the warping tendencies of irreplaceable components. In any case, it is important to evaluate the warpage of the substrate during heating from the time of development.
Issue with soldering
The behavior of solder, the transition from particle to liquid and then solid state, inside the reflow oven is delicate. Even a slight variation in conditions can cause the solder to behave unpredictably. As a result, a variety of solder-induced reflow soldering defects can occur. Many occur because the type and amount of solder and the temperature profile do not match the requirements specified by the selected components and the design of the board. Therefore, evaluations should focus on the solder and its quality in conjunction with the components and the PCB.
-
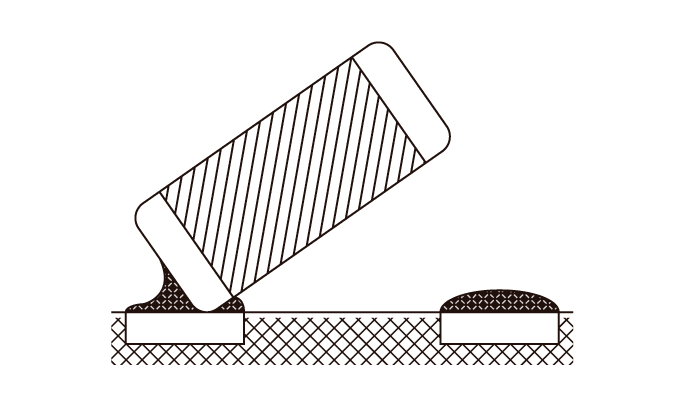 Tombstone
TombstoneDiscrepancies in the melting timing between the left and right solder and differences in the amount of solder cause tombstoning.
-
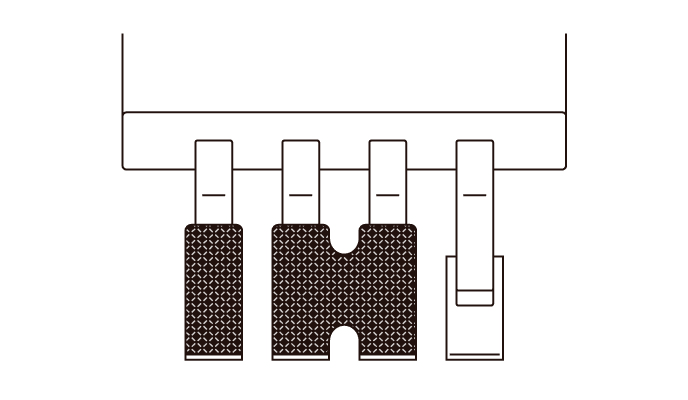 Solder Bridging
Solder BridgingWhen mounting narrow-pitch components, too much solder and excessive wetting and spreading can cause solder bridging.
-
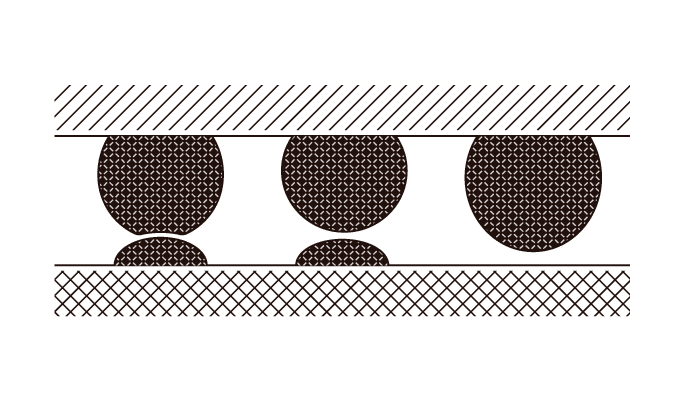 Non-wetting
Non-wettingThe wetting of solder to the terminals depends on the terminal shape, the plating type, and the solder used. Both insufficient and excessive wetting can result in mounting defects.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
-
Evaluating Solder Types
Solder properties vary depending on the composition, particle size, flux distribution, and other factors. Therefore, selecting the appropriate solder for the components and boards in use is essential. Observing and measuring behavior during the reflow process makes it possible to evaluate the compatibility of the solder with the components and boards and not just the solder itself.
-
Evaluating the Quantity of Solder
Excessive solder can lead to short circuits or bridging risks, while too little solder can result in openings. By observing and measuring the behavior during reflow, one can assess the amount of solder and its compatibility with the components and boards.
-
Evaluating Reflow soldering Conditions
If the reflow temperature is too high, it can significantly alter the shape of the components and boards, increasing risks of openings, cracks, and pillow soldering. Conversely, a low temperature might make the solder hard to melt, elevating the non-wetting risk. One can determine and set the optimal reflow conditions by observing the behavior during reflow.
The Cores Reflow SimulatorCORES Reflow Simulator
In 2002, we launched our core9030a, the world’s first reflow simulator to measure terminal flatness during heating. Since then, in response to the ever-evolving challenges at mounting sites, we have continued for over 20 years to develop our reflow simulators, selling to more than 300 companies around the globe.
Find Out MoreMore than
300
major domestic and international companies
Sony Corporation, Toyota Motor Corporation, Nintendo Corporation, Apple, Huawei, and Microsoft
More than
20 years of sales
Solution
Consulting
We believe the ultimate goal is not merely introducing equipment but enabling our customers to autonomously improve the mounting quality when installing it. Therefore, we directly engage with those facing challenges and offer solutions as partners, aiming to establish an enhanced quality system for mountings.
Find Out More

Direct CommunicationDirect Communication
Representatives from CORES directly consult with those responsible for implementation to understand their challenges and provide solutions and products. If you are grappling with immediate mounting defects or seeking medium-to-long-term mounting quality improvements, please contact CORES directly.
Web/Online Inquiry
フォームが表示されるまでしばらくお待ち下さい。
恐れ入りますが、しばらくお待ちいただいてもフォームが表示されない場合は、こちらまでお問い合わせください。
Inquiry by Telephone
Inquiry Desk
0422-24-7585
Taiwan Office (Chinese Language Support)
+886-906-680-216
Quality Control System
Connector manufacturers do not handle mounting directly, leading to a disparity in understanding between them and set manufacturers when tackling mounting defects. However, for set manufacturers, it is not just about product performance; the ease and reliability of mountings are equally crucial. Sometimes, a single component mounting defect can lead to a recall. Therefore, instead of solving problems after they occur, evaluating each process and creating a system to prevent reflow soldering defects is necessary.
Typical problematic scenarios
After mass production, a customer complains of reflow soldering defects.
After starting mass production, reflow soldering defects occur after delivery, leading to customer complaints. The company struggles to address these issues due to insufficient quality control measures, leading to complaints and subsequent losses in profit and trust.
Investigating reflow soldering quality during mass production
To swiftly resolve the issue, the company tries to ensure the quality of its products, given the reflow soldering conditions at the delivery site. However, lacking a proper evaluation system, the pressure continues to escalate.
Upholding reflow soldering quality based on company-established standards
Without an evaluation method, the company relies on its in-house standards, drawing from limited historical data. Unable to pinpoint the root cause, the relationship deteriorates as the question of responsibility remains ambiguous.

Ideal state
Preventive measures against reflow soldering defects prior to mass production
The company can prevent potential reflow soldering defect risks before manufacturing by evaluating the product under anticipated reflow soldering conditions during development and prototyping.

Monitoring quality variations during mass production
The quality of a material might change due to supplier variations, and often the purchaser is unaware of this. By conducting acceptance inspections, these shifts in quality can be detected early on, preventing potential reflow soldering defects.

Ensuring customer-based reflow soldering quality
Provide quality assurance to customers based on objective back data gathered before and during mass production. Should reflow soldering defects arise, quick resolutions can be achieved by leveraging analytical results and providing feedback to the development and manufacturing sectors and suppliers.


The key is to prevent reflow soldering defects preemptively rather than address them after they have emerged.
Problem &
SolutionReflow soldering Related issues and Solutions
Reflow soldering Quality of Terminal Coplanarity
Terminal coplanarity is crucial in the reflow soldering process. However, terminals are often evaluated and shipped based solely on their coplanarity at room temperature. When these terminals are subsequently heated during mounting, their flatness changes significantly, leading to reflow soldering defects. Ensuring consistent terminal coplanarity at room temperature and during heating, particularly near solder melting and solidification points, can prevent post-delivery mounting issues. Furthermore, as the warping of the housing during heating predominantly affects terminal coplanarity, gauging the extent and pattern of this warping is pivotal for quality enhancement.
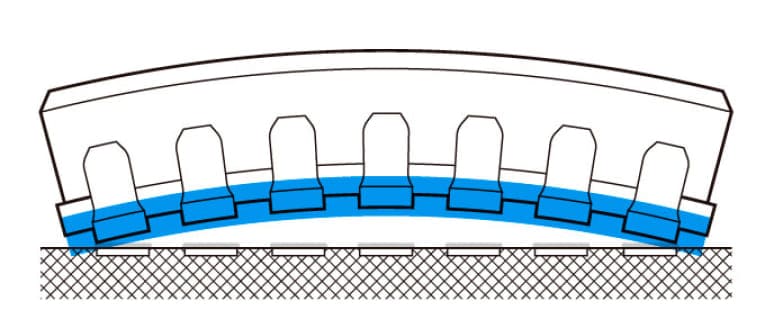
During heating, residual stress from the resin molding process is released, deforming the housing and impacting terminal coplanarity.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
The design, materials, resin molding conditions, and other factors determine the amount and tendency of housing warpage. Monitoring the housing behavior during reflow through 3D video visualization and providing feedback to development and manufacturing processes can enhance the reflow soldering quality.
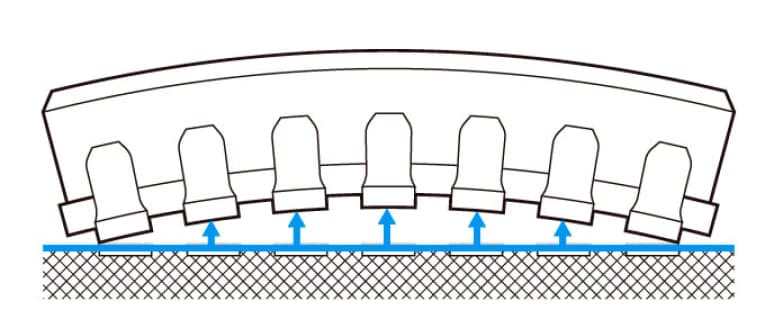
During reflow soldering, terminal copalanarity exceeding the solder thickness causes mounting defects, such as open, cracks, and pillow soldering.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
The center of gravity of the connector, its tilt from the mounting surface, and the heat transfer method can all influence the terminal flatness. Assessing the terminal coplanarity through heating and measurement techniques that replicate the reflow soldering environment is crucial for enhancing the reflow soldering quality.
Soldering Performance in SMT
The wettability of solder varies depending on the terminal shape and the type of plating. It also depends on the type of solder used, so quantitative evaluation based on the customer’s reflow soldering environment is necessary.
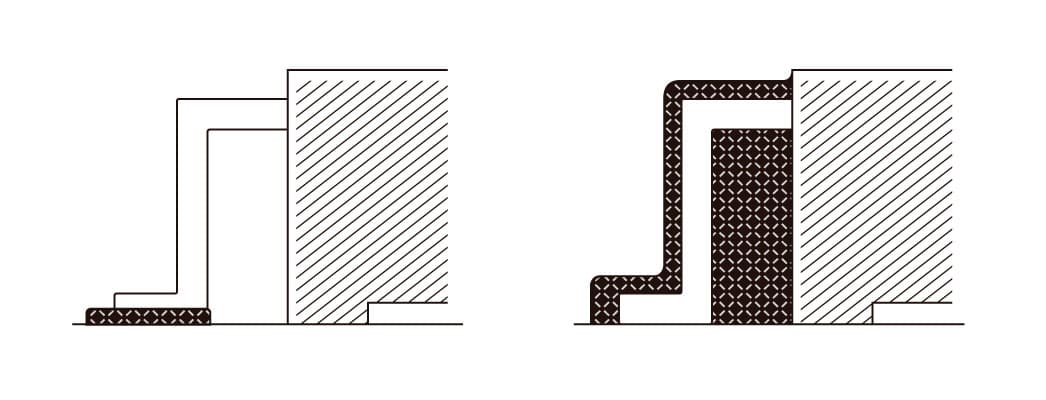
If the wetting properties of the solder are inadequate, it results in non-wetting, leading to reflow soldering defects such as open or pillow soldering defects. Furthermore, excessive wetting can allow solder and flux to penetrate into the terminals, leading to reflow soldering defects.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
Reflow soldering conditions vary depending on the customer’s product. A single in-house standard evaluation is insufficient in terms of quality assurance. Considerations for these conditions include the type and amount of solder and the reflow profile and atmosphere. We evaluate these conditions across a range of variations and monitor and measure them throughout the process. By doing so, it is possible to grasp the quality assurance line and provide feedback for development.
Quality of housing in SMT
When the housing is heated, residual stresses from the molding process are released, resulting in complex expansion. Beyond the expansion in the Z direction, which impacts terminal flatness, there is also expansion in the XY direction. Therefore, it must be evaluated in three dimensions.
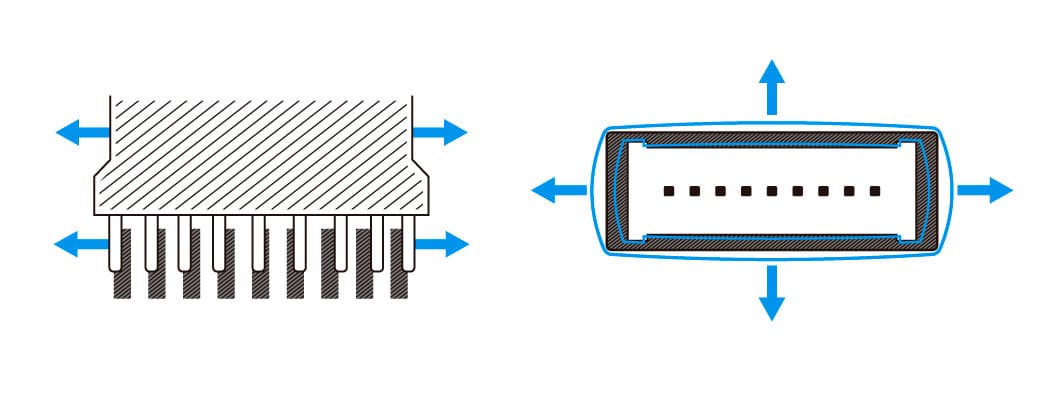
Expansion due to heating causes XY misalignment when terminals are displaced relative to the substrate pads because of XY deformation in the housing, which can also lead to mating failures due to deformation of the hood.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
For the quality control of housings, knowing the temperature they expand and how they expand is important. The important points are the preheat temperature, the peak temperature, and during cooling. Observing and measuring these changes during reflow allows us to define quality assurance parameters and offer actionable feedback for development.
The Cores Reflow SimulatorCORES Reflow Simulator
In 2002, we launched our core9030a, the world’s first reflow simulator to measure terminal flatness during heating. Since then, in response to the ever-evolving challenges at mounting sites, we have continued for over 20 years to develop our reflow simulators, selling to more than 300 companies around the globe.
Find Out MoreMore than
300
major domestic and international companies
Sumitomo Wiring Systems Ltd, Japan Aviation Electronics, HIROSE ELECTRIC CO LTD, Foxconn Interconnect technology Ltd, and TE Connectivity Ltd
More than
20 years of sales
Solution
ConsultingSolution Consulting
We believe the ultimate goal is not merely introducing equipment but enabling our customers to autonomously improve the mounting quality when installing it. Therefore, we directly engage with those facing challenges and offer solutions as partners, aiming to establish an enhanced quality system for mountings.
Find Out More

Direct CommunicationDirect Communication
Representatives from CORES directly consult with those responsible for implementation to understand their challenges and provide solutions and products. If you are grappling with immediate mounting defects or seeking medium-to-long-term mounting quality improvements, please contact CORES directly.
Web/Online Inquiry
フォームが表示されるまでしばらくお待ち下さい。
恐れ入りますが、しばらくお待ちいただいてもフォームが表示されない場合は、こちらまでお問い合わせください。
Inquiry by Telephone
Inquiry Desk
0422-24-7585
Taiwan Office (Chinese Language Support)
+886-906-680-216
Quality Control System
Semiconductor manufacturers do not handle the reflow soldering process directly. Therefore, there exists a disparity in understanding between them and set manufacturers confronting mounting defects. However, for set manufacturers, quality is important not only in terms of product performance but also in terms of problem-free reflow soldering. Occasionally, a defect in reflow soldering just one component can lead to a product recall. Therefore, instead of solving problems after they occur, evaluating each process and creating a system to prevent reflow soldering defects is necessary.
Typical problematic scenarios
After mass production, a customer complains of reflow soldering defects.
After starting mass production, reflow soldering defects occur after delivery, leading to customer complaints. The company struggles to address these issues due to insufficient quality control measures, leading to complaints and subsequent losses in profit and trust.

Investigating reflow soldering quality during mass production
To swiftly resolve the issue, the company tries to ensure the quality of its products, given the reflow soldering conditions at the delivery site. However, lacking a proper evaluation system, the pressure continues to escalate.

Upholding reflow soldering quality based on company-established standards
Without an evaluation method, the company relies on its in-house standards, drawing from limited historical data. Unable to pinpoint the root cause, the relationship deteriorates as the question of responsibility remains ambiguous.

Ideal state
Preventive measures against reflow soldering defects prior to mass production
The company can prevent potential reflow soldering defect risks before manufacturing by evaluating the product under anticipated reflow soldering conditions during development and prototyping.

Monitoring quality variations during mass production
The quality of a material might change due to supplier variations, and often the purchaser is unaware of this. By conducting acceptance inspections, these shifts in quality can be detected early on, preventing potential reflow soldering defects.

Ensuring customer-based reflow soldering quality
Provide quality assurance to customers based on objective back data gathered before and during mass production. Should reflow soldering defects arise, quick resolutions can be achieved by leveraging analytical results and providing feedback to the development and manufacturing sectors and suppliers.


The key is to prevent reflow soldering defects preemptively rather than address them after they have emerged.
Problem &
SolutionReflow soldering-Related issues and Solutions
The Mounting Quality of the Terminal Flatness
Terminal coplanarity is crucial in the reflow soldering process. However, terminals are often evaluated and shipped based solely on their coplanarity at room temperature. When these terminals are subsequently heated during reflow soldering, their coplanarity changes significantly, leading to reflow soldering defects. Ensuring consistent terminal coplanarity at room temperature and during heating, particularly near solder melting and solidification points, can prevent post-delivery reflow soldering issues. Furthermore, as the warping of the package during heating predominantly affects terminal coplanarity, gauging the extent and pattern of this warping is pivotal for quality enhancement.
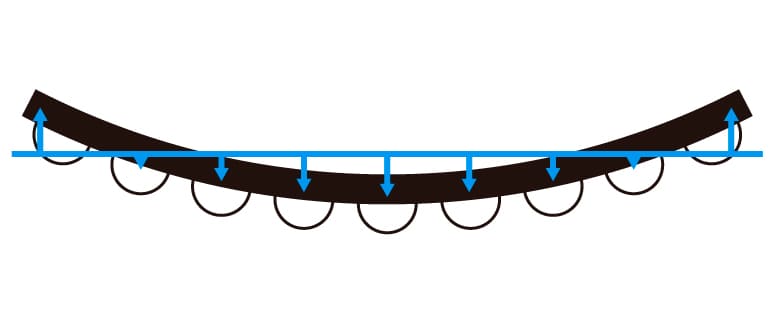
During heating, residual stress from the resin molding process is released, deforming the housing and impacting terminal coplanarity.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
The design, materials, resin molding conditions, and other factors determine the amount and tendency of housing warpage. Monitoring the housing behavior during reflow through 3D video visualization and providing feedback to development and manufacturing processes can enhance the reflow soldering quality.
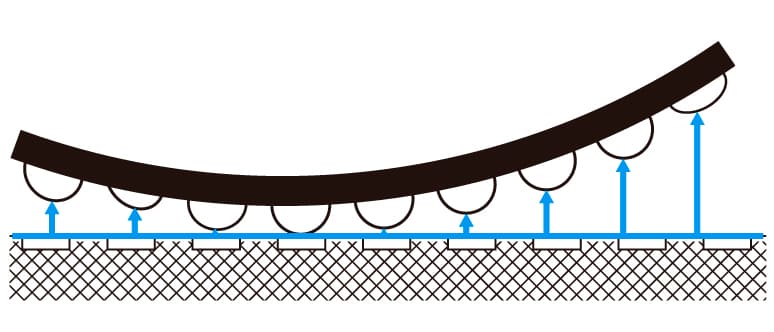
During reflow soldering, terminal copalanarity exceeding the solder thickness causes mounting defects, such as open, cracks, and pillow soldering.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
The center of gravity of the IC, its tilt from the mounting surface, and the heat transfer method can all influence the terminal flatness. Assessing the terminal coplanarity through heating and measurement techniques that replicate the reflow soldering environment is crucial for enhancing the reflow soldering quality.
Soldering Performance in SMT
The wettability of solder varies depending on the terminal shape and the type of plating. It also depends on the type of solder used, so quantitative evaluation based on the customer’s reflow soldering environment is necessary.
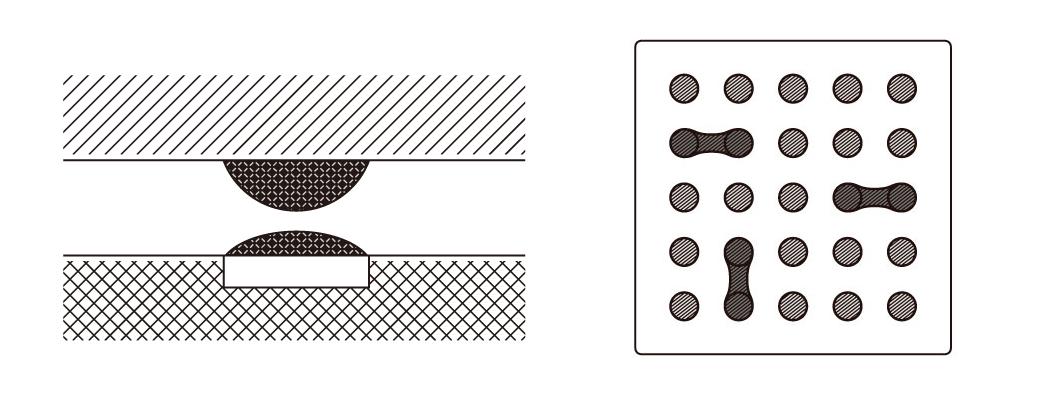
If the wetting properties of the solder are inadequate, it results in non-wetting, leading to mounting defects such as openings or pillow soldering defects. However, excessively increasing the amount of solder can lead to it spreading horizontally, resulting in bridging when the solder softens upon heating.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
If the terminal has good solder wettability, less solder is required. However, poor wettability can lead to non-wetting. Increasing the amount of solder to address this increases the risk of bridging. Therefore, we evaluate the customer’s mounting environment, such as the temperature profile and solder type, and we evaluate the behavior of the solder during reflow. By doing so, it is possible to understand the quality assurance line and provide feedback for development.
Quality of package sealing in SMT
Packages comprise laminated components with distinct characteristics, such as molds, substrates, and adhesives. Slight variations in conditions can result in delamination or other issues during mounting. Therefore, evaluations based on the customer’s reflow soldering environment are necessary.
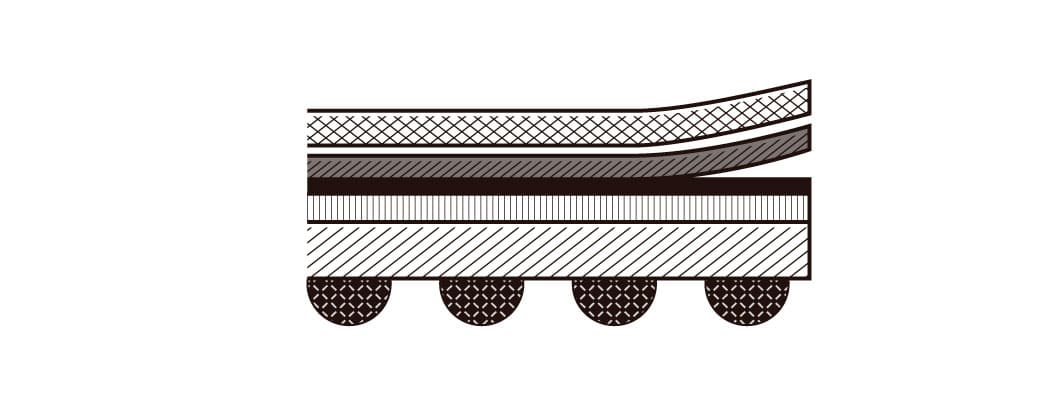
Package delamination will occur if the substrate warps when heated and the mold and adhesive soften.

Analysis Solutions and Target Products
For the quality control of packages, it is important to know how a component reacts at different temperatures. By understanding the transition points at each temperature and observing and measuring their changes during reflow, it is possible to maintain quality assurance and provide valuable feedback for development.
The Cores Reflow SimulatorCORES Reflow Simulator
In 2002, we launched our core9030a, the world’s first reflow simulator to measure terminal flatness during heating. Since then, in response to the ever-evolving challenges at mounting sites, we have continued for over 20 years to develop our reflow simulators, selling to more than 300 companies around the globe.
Find Out MoreMore than
300
major domestic and international companies
Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation, HiSilicon Technologies Co Ltd, Nintendo Corporation, Infineon Technologies AG, Intel Corporation, Micron Technology Inc, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited
More than
20 years of sales
Solution
ConsultingSolution Consulting
We believe the ultimate goal is not merely introducing equipment but enabling our customers to autonomously improve the mounting quality when installing it. Therefore, we directly engage with those facing challenges and offer solutions as partners, aiming to establish an enhanced quality system for mountings.
Find Out More

Direct CommunicationDirect Communication
Representatives from CORES directly consult with those responsible for implementation to understand their challenges and provide solutions and products. If you are grappling with immediate mounting defects or seeking medium-to-long-term mounting quality improvements, please contact CORES directly.
Web/Online Inquiry
フォームが表示されるまでしばらくお待ち下さい。
恐れ入りますが、しばらくお待ちいただいてもフォームが表示されない場合は、こちらまでお問い合わせください。
Inquiry by Telephone
Inquiry Desk
0422-24-7585
Taiwan Office (Chinese Language Support)
+886-906-680-216


